Premium Only Content
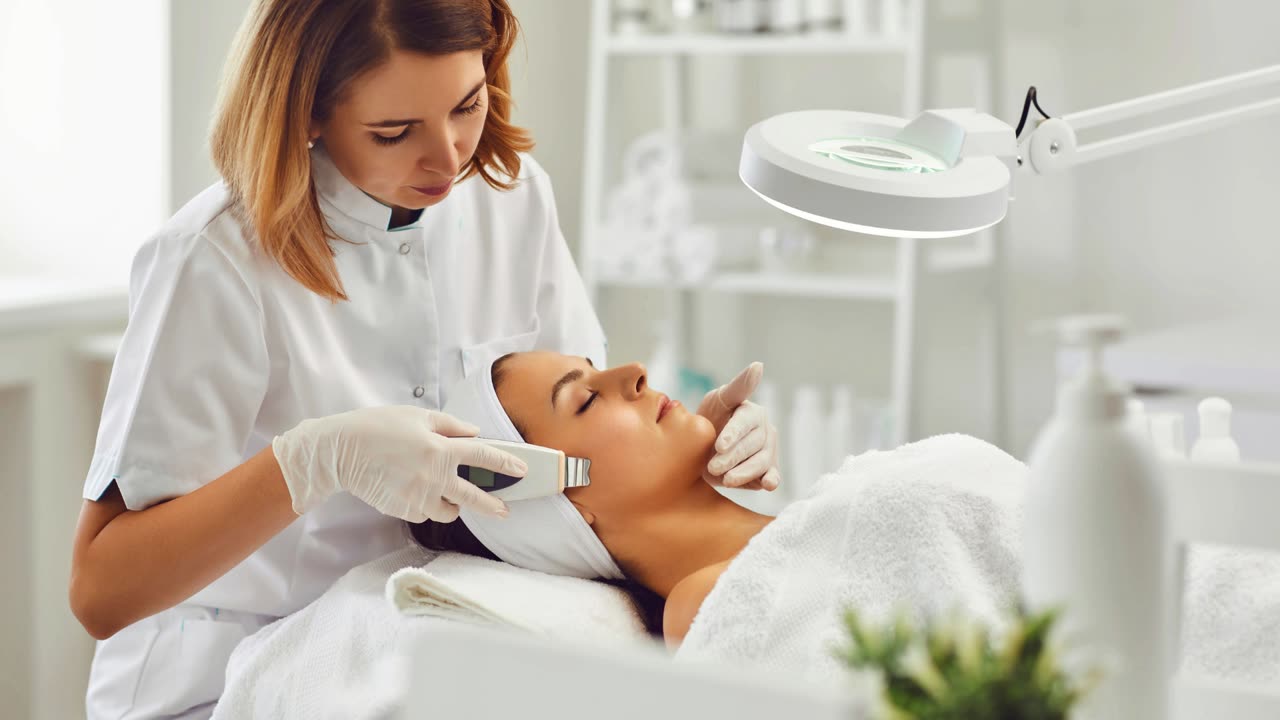

Artificial Intelligence or AI in Clinical Applications - Part 1
Cardiovascular:
Artificial intelligence algorithms have shown promising results in accurately diagnosing and risk stratifying patients with concern for coronary artery disease, showing potential as an initial triage tool. Other algorithms have been used in predicting patient mortality, medication effects, and adverse events following treatment for acute coronary syndrome. Wearables, smartphones, and internet-based technologies have also shown the ability to monitor patients' cardiac data points, expanding the amount of data and the various settings AI models can use and potentially enabling earlier detection of cardiac events occurring outside of the hospital. Another growing area of research is the utility of AI in classifying heart sounds and diagnosing valvular disease. Challenges of AI in cardiovascular medicine have included the limited data available to train machine learning models, such as limited data on social determinants of health as they pertain to cardiovascular disease.
A key limitation in early studies evaluating AI were omissions of data comparing algorithmic performance to humans. Examples of studies which assess AI performance relative to physicians includes how AI is non-inferior to humans in interpretation of cardiac echocardiograms and that AI can diagnose heart attack better than human physicians in the emergency setting, reducing both low-value testing and missed diagnoses.
In cardiovascular tissue engineering and organoid studies, AI is increasingly used to analyze microscopy images, and integrate electrophysiological read outs.
Dermatology:
Medical imaging (such as X-ray and photography) is a commonly used tool in dermatology and the development of deep learning has been strongly tied to image processing. Therefore, there is a natural fit between the dermatology and deep learning. Machine learning learning holds great potential to process these images for better diagnoses. Han et al. showed keratinocytic skin cancer detection from face photographs. Esteva et al. demonstrated dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer from lesion images. Noyan et al. demonstrated a convolutional neural network that achieved 94% accuracy at identifying skin cells from microscopic Tzanck smear images. A concern raised with this work is that it has not engaged with disparities related to skin color or differential treatment of patients with non-white skin tones.
Life Goals Achievement Success Guides. As well as helping you defeat: Lack of focus | Fear of failure | Lack of commitment | Lack of a plan | Procrastination | Lack of confidence | Analysis paralysis | Unrealistic goals | Lack of motivation. So you can live the life you love and love the life you live.
Visit us - https://breakouttools.com
-
 19:05
19:05
Michael Feyrer Jr
22 hours agoCan you even fit this much FAIL in one video? $10K Challenge Week 1
8 -
 19:53
19:53
Professor Nez
15 hours agoYou WON’T BELIEVE What I Found on Charlie Kirk’s Shooter!
89114 -
 1:35:53
1:35:53
The China Show
16 hours agoBrutal Mayhem in China as Dark Coverups are Exposed - #280
75 -
 12:30:34
12:30:34
Times Now World
22 hours agoLIVE | Russia-Belarus Zapad-2025 LIVE | Missiles Target NATO in Arctic & Baltic
3.55K1 -
 32:14
32:14
daniellesmithab
17 hours agoNew Feature for Driver’s Licence and ID Cards
22.6K6 -
 2:54:40
2:54:40
FreshandFit
14 hours agoChat Makes Pothead RAGE QUIT!!!
480K79 -
 1:32:34
1:32:34
Badlands Media
16 hours agoBaseless Conspiracies Ep. 150: 9/11 Mysteries, Remote Pilots, and Hidden Agendas
95.2K36 -
 5:32:35
5:32:35
Akademiks
8 hours agoWHERE IS WHAM????? Thug we Forgive u dawg.. Ralo vs Boosie. Charlie Kirk fallout. Cardi B album?
78.1K7 -
 2:05:53
2:05:53
Inverted World Live
9 hours agoDeath Cult Terror Cells, NASA Bans Chinese Nationals | Ep. 108
72.2K14 -
 2:43:57
2:43:57
TimcastIRL
10 hours agoVP Says No Unity With Democrats Celebrating Charlie Kirk Assassination, Left Confirmed | Timcast IRL
300K199