Premium Only Content
This video is only available to Rumble Premium subscribers. Subscribe to
enjoy exclusive content and ad-free viewing.
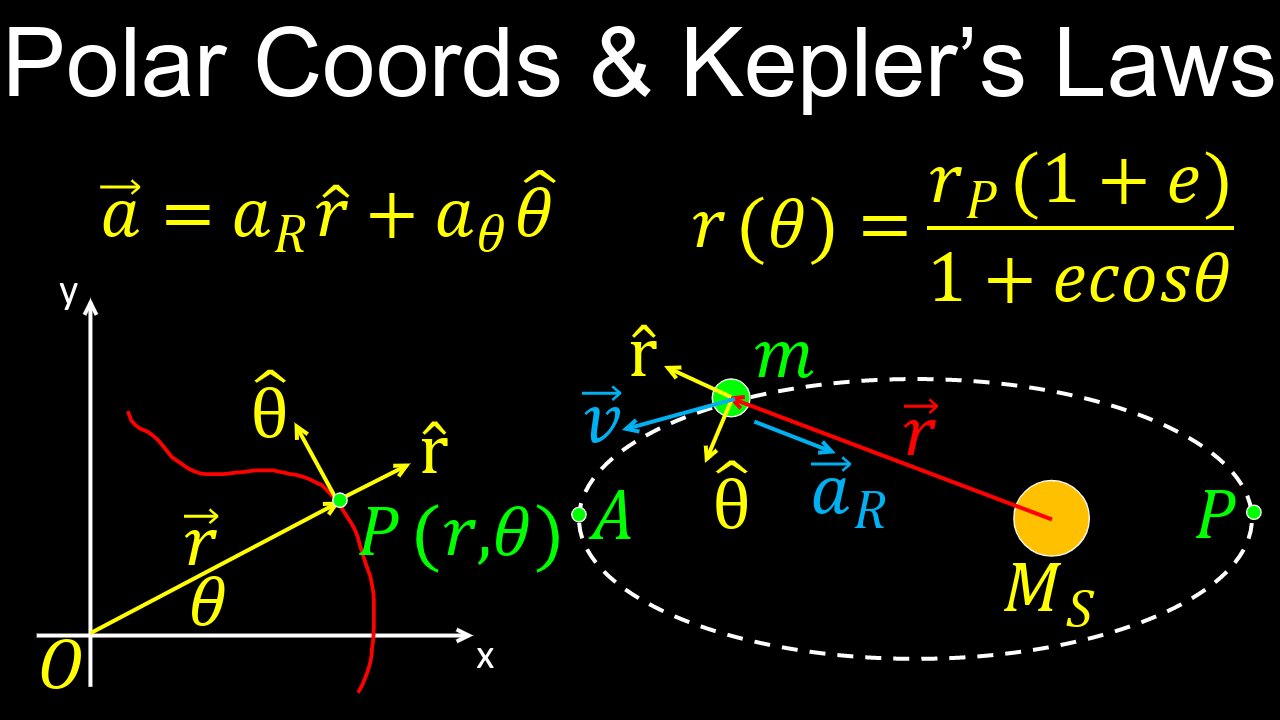
Motion in Polar Coordinates, Kepler's Laws, Worked Examples - Calculus 3
6 months ago
61
Health & Science
Education
calculus 3
polar coordinates
motion in plane
kepler's laws of planetary motion (namesake)
kepler's laws of planetary motion
kepler's laws of planetary motion (literature subject)
dynamics polar coordinates
kepler's laws
calculus
This video explains motion (velocity and acceleration) in polar and cylindrical coordinates for particles moving in the plane and 3D space, proves the orbit of a planet around a star is planar, how to derive Kepler's first (elliptical orbit), second (equal areas or conservation of angular momentum) and third law (orbital period) for planetary orbits. You will be able to explain why a leap year has 366 days.
0:00 Motion in polar coordinates
6:08 Motion in cylindrical polar coordinates
7:50 Proving the orbit of a planet around a star is planar
13:45 Deriving Kepler's first law
28:28 Deriving Kepler's second law
33:35 Deriving Kepler's third law
41:06 Worked examples
Loading comments...
-
 DVR
DVR
Stephen Gardner
35 minutes ago💣 Trump White House UNEXPECTED Move + Thune DESTROYS Schumer on Senate Floor!!
2281 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Lara Logan
9 hours agoSHOTS FIRED: The Tyranny of Big Pharma Exposed with Dr. Sherri Tenpenny | EP 42 | Lara Logan
666 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Playback Request Live
52 minutes agoPRL LIVE @ DREAMHACK!!
63 watching -
 1:03:55
1:03:55
Sean Unpaved
2 hours agoRavens' Resurrection Night: Lamar Buries Miami, NFL/CFB Spooky HC Shifts, & Kalshi's Week 9/10 Odds!
17.7K -
 2:16:48
2:16:48
Film Threat
1 day agoHALLOWEEN HORROR + BACK TO THE FUTURE RERELEASE + MORE REVIEWS | Film Threat Livecast
7.99K -
 1:21:16
1:21:16
Steven Crowder
5 hours ago10th Annual Halloween Spooktacular: Reacting to the 69 Gayest Horror Movies of All Time
258K144 -
 57:39
57:39
The Rubin Report
4 hours agoKamala Gets Visibly Angry as Her Disaster Interview Ends Her 2028 Election Chances
39.5K56 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Dr Disrespect
4 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - ARC RAIDERS - DANGEROUS ADVENTURES (LEVEL 12)
1,497 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
17 hours agoLIVE & BREAKING NEWS! | FRIDAY 10/31/25
1,930 watching -
 1:36:11
1:36:11
The Mel K Show
3 hours agoHunters Become the Hunted: A Reckoning Is Finally Coming - 10/31/25
22.5K14