Premium Only Content
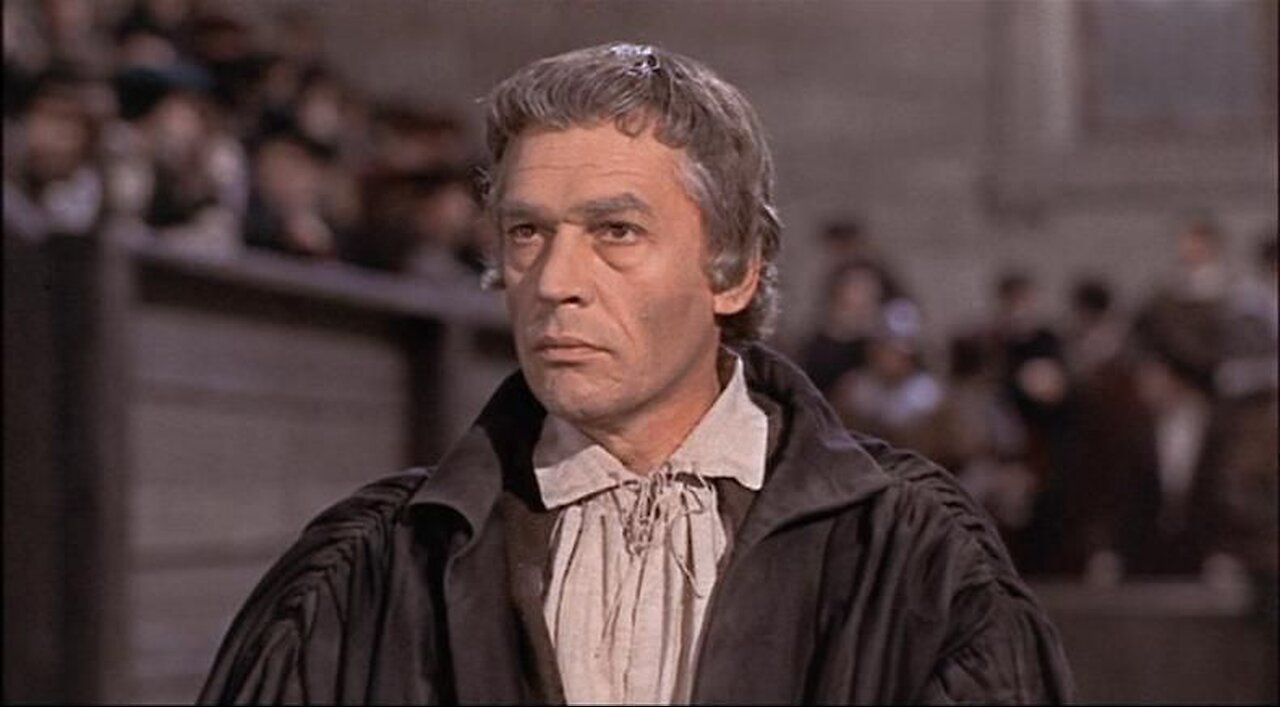

"A Moral Squint", (a Virtue or a Curse)
Are you a "Man for All Seasons"? Do you have the courage of your convictions?
A moral squint refers to the tendency to emphasize moral considerations over practical or political solutions. It is often associated with moral integrity, where individuals minimize their state duties or directives versus matters of their personal conscience. For example, in the context of Cardinal Wolsey and Thomas More, Wolsey expresses frustration with More's moral stance, suggesting that he should see facts without a moral squint, indicating that More's moral standards are too high for practical matters. This concept can also be seen in discussions about moral relativism, where individuals may justify actions based on their moral beliefs, even if those beliefs are not universally accepted.
Thomas Wolsey (March 1473– 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic cardinal. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the controlling figure in virtually all matters of state. He also held important ecclesiastical appointments. These included the Archbishop of York—the second most important role in the English church—and that of papal legate. His appointment as a cardinal by Pope Leo X in 1515 gave him precedence over all other English clergy.
The highest political position Wolsey attained was Lord Chancellor, the king's chief adviser (formally, as his successor and disciple Thomas Cromwell was not). In that position, he enjoyed great freedom and was often depicted as the alter rex ("other king"). After failing to negotiate an annulment of Henry's marriage to Catherine of Aragon, Wolsey fell out of favor and was stripped of his government titles.
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, theologian, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lord Chancellor from October 1529 to May 1532. He wrote Utopia, published in 1516, which describes the political system of an imaginary island state.
More opposed the Protestant Reformation, directing polemics against the theology of Martin Luther, Huldrych Zwingli and William Tyndale. More also opposed Henry VIII's separation from the Catholic Church, refusing to acknowledge Henry as supreme head of the Church of England and the annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. After refusing to take the Oath of Supremacy, he was convicted of treason on what he stated was false evidence and was executed. At his execution, he was reported to have said: "I die the King's good servant, and God's first."
Thomas Cromwell (1485 – 28 July 1540) was an English statesman and lawyer who served as chief minister to King Henry VIII from 1534 to 1540, when he was beheaded on orders of the king, who later blamed false charges for the execution.
Cromwell was one of the most powerful proponents of the English Reformation. As the king's chief secretary, he instituted new administrative procedures that transformed the workings of government. He helped to engineer an annulment of the King's marriage to Catherine of Aragon so that Henry could lawfully marry Anne Boleyn. Henry failed to obtain the approval of Pope Clement VII for the annulment in 1533, so Parliament endorsed the king's claim to be Supreme Head of the Church of England, giving him the authority to annul his own marriage. Cromwell subsequently charted an evangelical and reformist course for the Church of England from the unique posts of Vicegerent in Spirituals and Vicar-general (the two titles refer to the same position).
Henry VIII (28 June 1491 – 28 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement with Pope Clement VII about such an annulment led Henry to initiate the English Reformation, separating the Church of England from papal authority. He appointed himself Supreme Head of the Church of England and dissolved convents and monasteries, for which he was excommunicated by the pope.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Game On!
17 hours ago $2.07 earnedAnother FOOTBALL FRIDAY! Weekend Preview And BEST BETS!
298 watching -
 31:55
31:55
ZeeeMedia
18 hours agoHow Gold & Silver Fight Against Digital ID ft. Bill Armour | Daily Pulse Ep 148
7.26K8 -
 13:29
13:29
Clintonjaws
14 hours ago $15.01 earnedCNN Host Stops Show & Plays Surprise Clip Forcing Democrat To Correct Lie
31.5K12 -
 14:55
14:55
World2Briggs
18 hours ago $1.91 earnedThe 10 U.S. Cities Americans Can No Longer Afford — 2025 Edition
9.91K -
 8:19
8:19
Millionaire Mentor
17 hours agoATC Whistleblower EXPOSES Obama’s Dirty FAA Secret
13.4K8 -
 LIVE
LIVE
BEK TV
23 hours agoTrent Loos in the Morning - 11/21/2025
184 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Bubba Army
22 hours agoCHICAGO SUBWAY FIRE ATTACK - Bubba the Love Sponge® Show | 11/21/25
1,673 watching -
 57:31
57:31
Side Scrollers Podcast
17 hours agoBlabs VS DuckTales
12.9K10 -
 8:52
8:52
MetatronGaming
14 hours agoOverwatch 2 New Hero Vendetta La Lupa
116K10 -
 1:37:16
1:37:16
omarelattar
23 hours agoEx-Mafia Boss: I Made $8 Million Every Week Until The FBI Destroyed My Life! What I Learned...
28.7K2