Premium Only Content
The Johari Window Model
Theories of Communication, self-assessment as well as macro societal views.
History:
It is necessary to improve self-awareness and personal development among individuals when they are in a group. The ‘Johari’ window model is a convenient method used to achieve this task of understanding and enhancing communication between the members in a group. American psychologists Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham developed this model in 1955. The idea was derived as the upshot of the group dynamics in University of California and was later improved by Joseph Luft. The name ‘Johari’ came from joining their first two names. This model is also denoted as feedback/disclosure model of self-awareness.
Introduction:
The Johari window model is used to enhance the individual’s perception on others. This model is based on two ideas- trust can be acquired by revealing information about you to others and learning yourselves from their feedback. Each person is represented by the Johari model through four quadrants or windowpane. Each four windowpanes signify personal information, feelings, motivation and whether that information is known or unknown to oneself or others in four viewpoints.
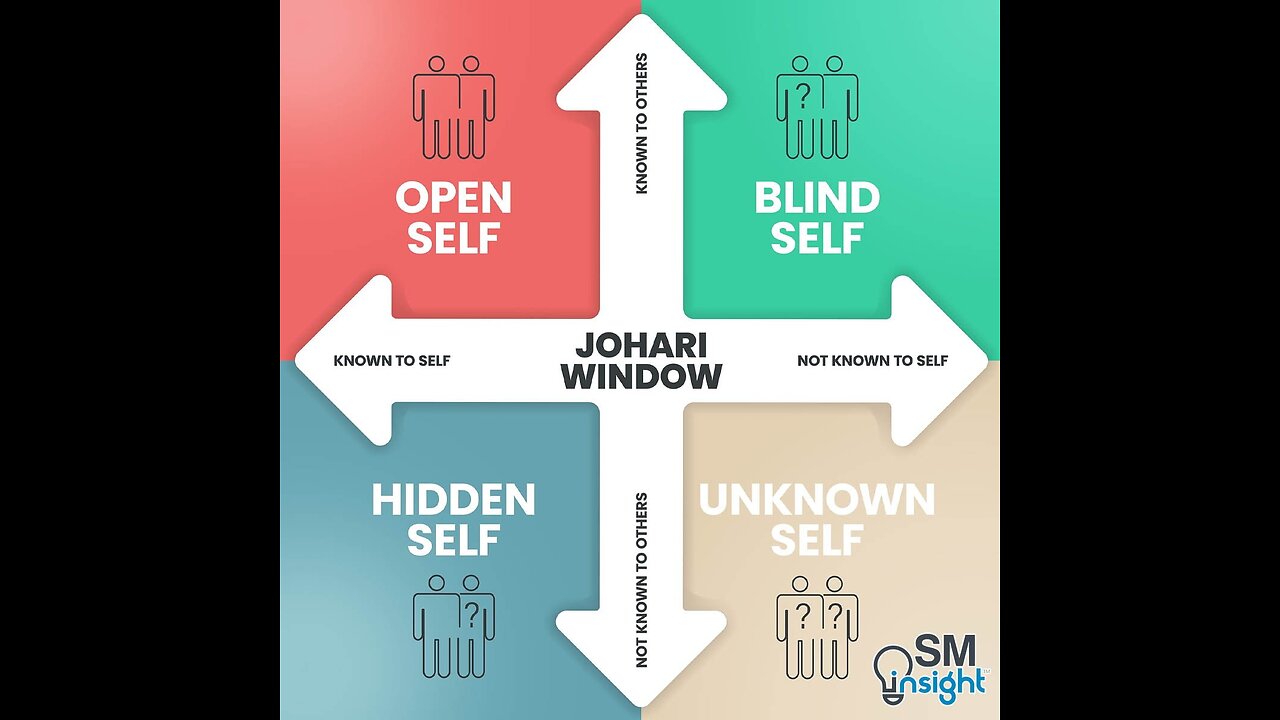
The Johari Window Model:
The method of conveying and accepting feedback is interpreted in this model. A Johari is represented as a common window with four panes. Two of these panes represent self and the other two represent the part unknown to self but to others. The information transfers from one pane to the other as the result of mutual trust which can be achieved through socializing and the feedback got from other members of the group.
1. Open/self-area or arena
2. Blind self or blind spot
3. Hidden area or façade
4. Unknown area
Please subscribe to my Substack Channel:
https://juxtaposition1.substack.com/podcast
-
 34:58
34:58
Rehypothecation1
21 hours agoInternecine, (a tutorial)
2841 -
 13:36
13:36
Clintonjaws
1 day agoCBC 2024 Election Night - Highlights - This Is Priceless!
1.13K10 -
 LIVE
LIVE
GamerGril
3 hours agoIt's The Zombie Apocalypse, Bring Your Friends 💞Scream Queens💞
53 watching -
 23:20
23:20
Lady Decade
3 hours agoI Spent The Night With Alex Jones
2.49K13 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Phyxicx
2 hours agoHalo Tournament! - 10/25/2025
30 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
megimu32
4 hours agoOFF THE SUBJECT: Zombie Apocalypse with GamerGril & Friends 🧟 ♀ (Send Help)
1,091 watching -
 22:08
22:08
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
22 hours agoUnder Prague
36.1K15 -
![[LIVE] Halo 3 | PhyxicxGaming Halo 3 Draft to 4v4s Tournament!](https://1a-1791.com/video/fwe2/be/s8/1/6/b/O/t/6bOtz.0kob-small-LIVE-Halo-3-PhyxicxGaming-H.jpg) LIVE
LIVE
Joke65
2 hours ago[LIVE] Halo 3 | PhyxicxGaming Halo 3 Draft to 4v4s Tournament!
37 watching -
 4:43:07
4:43:07
Grant Cardone
8 hours agoGrant Cardone EXPOSES How the 1% REALLY Build Wealth (LIVE)
198K8 -
 1:19:20
1:19:20
Jeff Ahern
5 hours ago $13.61 earnedThe Saturday Show with Jeff Ahern
19.2K9