Premium Only Content
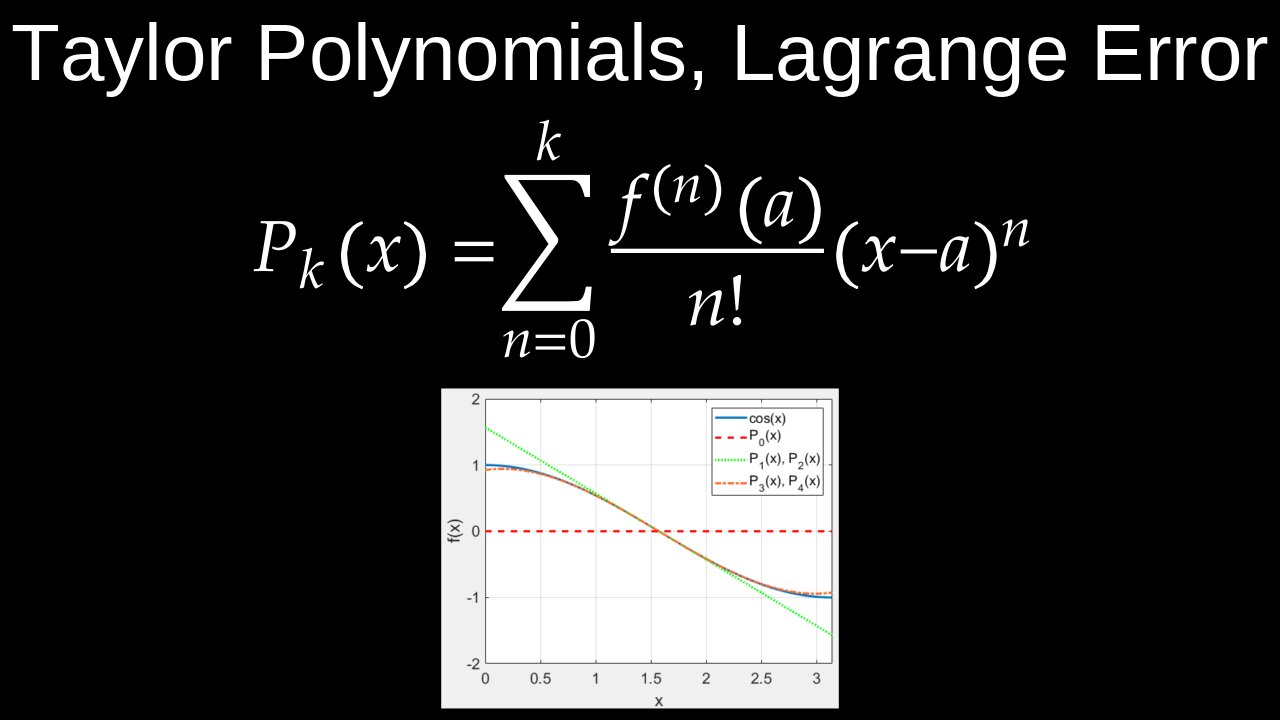
Taylor Polynomials, Approximating Functions, Lagrange Error Bound, Remainder, Examples - Calculus
Taylor polynomials are used to approximate functions, and the Lagrange error bound (also known as the remainder term) provides an upper limit on the error of that approximation. The formula is \(|R_{n}(x)|\le \frac{M}{(n+1)!}|x-c|^{n+1}\), where \(R_{n}(x)\) is the error, \(n\) is the degree of the Taylor polynomial, \(c\) is the center of the polynomial, \(x\) is the point where the function is being approximated, and \(M\) is the maximum value of the absolute value of the $(n+1)$th derivative of the function on the interval between \(c\) and \(x\).
💡Taylor Polynomials
• A Taylor polynomial is a polynomial approximation of a function at a specific point (the center).
• The accuracy of the approximation generally increases as the degree of the polynomial increases.
• The formula for a Taylor polynomial of degree \(n\) centered at \(a\) is:
\(T_{n}(x)=\sum _{k=0}^{n}\frac{f^{(k)}(a)}{k!}(x-a)^{k}\)
💡Lagrange Error Bound
• The Lagrange error bound gives the maximum possible error for a Taylor polynomial approximation.
• It is based on the $(n+1)$th derivative of the function, as the error is directly related to the next term in the full Taylor series.
• The formula is:
\(|R_{n}(x)|\le \frac{M}{(n+1)!}|x-c|^{n+1}\)
• Breakdown of the formula:
◦ \(|R_{n}(x)|\): The absolute value of the Lagrange remainder (the error).
◦ \(M\): The maximum absolute value of the $(n+1)$th derivative, \(f^{(n+1)}(z)\), for any \(z\) in the interval between \(c\) and \(x\).
◦ \(n\): The degree of the Taylor polynomial being used.
◦ \(c\): The center of the Taylor series.
◦ \(x\): The value at which the function is being approximated.
💡How they are used together
• When a function is approximated by a Taylor polynomial, the Lagrange error bound helps you determine how far off your approximation might be.
• By finding the maximum value of the $(n+1)$th derivative, you can calculate an upper limit for the error using the formula.
• This is useful for both verifying the accuracy of an approximation and for determining what degree of polynomial is needed to achieve a desired level of precision.
💡Worksheets are provided in PDF format to further improve your understanding:
• Questions Worksheet: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1DlYi7xcmyEAhWTnwUN8zRgisBdHIdmtr/view?usp=drive_link
• Answers: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VEHFVDs67vvvQVVsozjmOCO5RbEgzbkA/view?usp=drive_link
💡Chapters:
00:00 Taylor polynomial, with example
03:36 Lagrange Error Bound, with example
🔔Don’t forget to Like, Share & Subscribe for more easy-to-follow Calculus tutorials.
🔔Subscribe: https://rumble.com/user/drofeng
_______________________
⏩Playlist Link: https://rumble.com/playlists/Ptm8YeEDb_g
_______________________
💥 Follow us on Social Media 💥
🎵TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@drofeng?lang=en
𝕏: https://x.com/DrOfEng
🥊: https://youtube.com/@drofeng
-
 LIVE
LIVE
vivafrei
4 hours agoEp. 295: "Maryland Man" Freed; Jan. 6 PATSY? SCOTUS Rulings GALORE! Shawn Ryan Threat & MORE!
9,914 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
GamerGril
1 hour agoBlocking Chainsaw Attacks With My Arm 💕Resident Evil 7💕
179 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
GrimmHollywood
5 hours ago🔴LIVE • GRIMM HOLLYWOOD • GRIMMBAS • DAY 2 of 12 • KINGDOM COME DELIVERANCE II DLC •
240 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
ttvglamourx
4 hours ago $4.42 earnedPLAYING WITH VIEWERS !DISCORD
584 watching -
 38:45
38:45
Tactical Advisor
3 hours agoQuitting my Job & Giveaway Winner! | Vault Room Live Stream 010
10.7K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
ItzSufari
1 hour ago🔴The Lords Sunday - Come join us in prayer - Amen
56 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
BenderOdoyle
3 hours agoBO7 - with Friends, The Return
32 watching -
 17:17
17:17
Fit'n Fire
3 hours ago $0.31 earnedDraco Owners Won't Like This...Zastava M85 & M92 Are Better
4.33K2 -
 LIVE
LIVE
NSSKEnt
6 hours ago5 Mil Easy | Max Level EASY | ARC Raiders
43 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Sami Mikata
2 hours agoZombie Army 4 Dead War Live Stream
63 watching