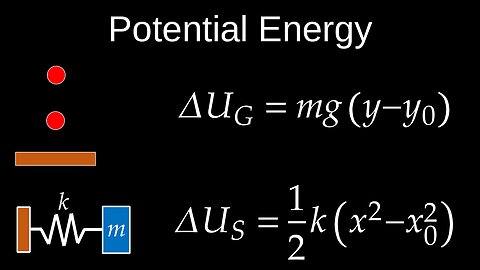Premium Only Content
Vectors Vs Scalars, Displacement, Distance, Velocity, Speed, Acceleration - Physics (Mechanics)
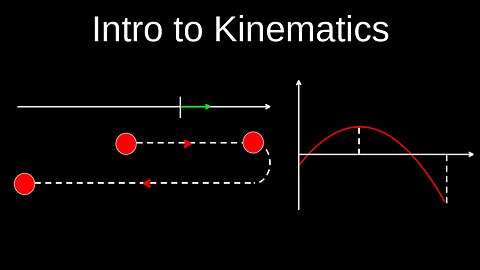
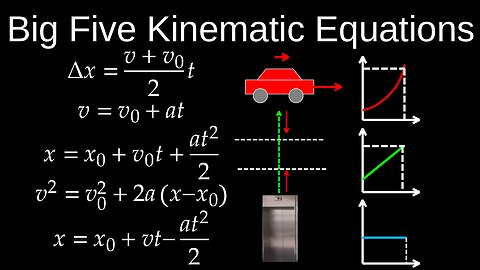
Big Five Kinematics, Uniform Acceleration, How to Select, Intervals, Objects - Physics (Mechanics)
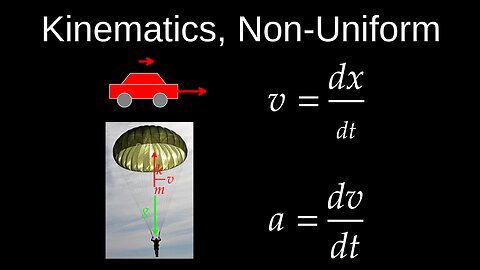
Kinematics, Non-Uniform Motion, Non-Constant Acceleration, 1D Motion - Physics (Mechanics)
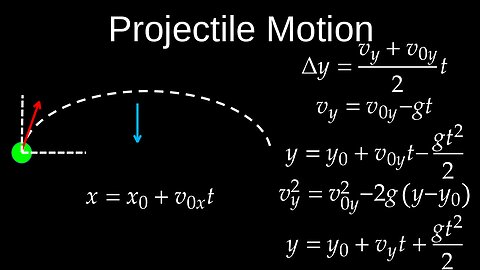
Projectile Motion, Kinematics, 2D Motion, Problems, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
Reference Frames, Relative Motion, Velocity, Vectors, Questions, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
Vectors, Addition, Scaling, Negation, Subtraction, Coord Systems - Physics (Mechanics)
Newton's Second Law of Motion, First Law, Equations, Worksheet, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
Friction, Resistive Force, Equation, Inclined Plane Motion, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
Cables and Pulleys, Massless, Atwood Machines, Free Body Diagrams - Physics (Mechanics)
Resistive Forces, Drag, Terminal Velocity, Example - Physics (Mechanics)
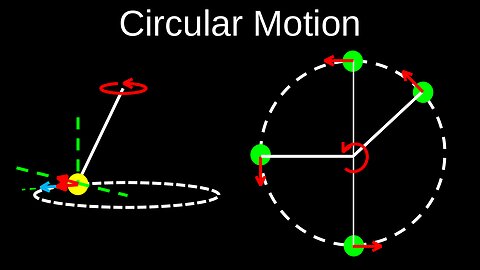
Circular Motion, Centripetal Acceleration, Vertical, Horizontal, Banked - Physics (Mechanics)
Newton's Third Law of Motion, Equal and Opposite Forces, Action Reaction Pairs - Physics (Mechanics)
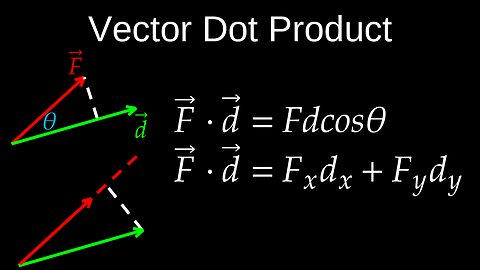
Vector Dot Product, Commutativity, Projection, Visualization, Proof - Physics (Mechanics)
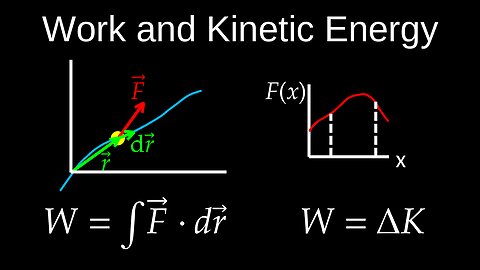
Work of a Force, Dot Product, Integral, Work Energy Theorem, Kinetic Energy - Physics (Mechanics)
Potential Energy, Gravity, Elastic, Spring, Conservative Forces, Functions - Physics (Mechanics)
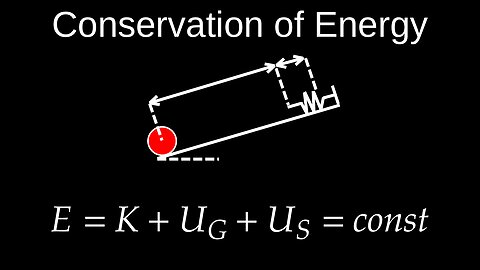
Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Conservative Systems - Physics (Mechanics)
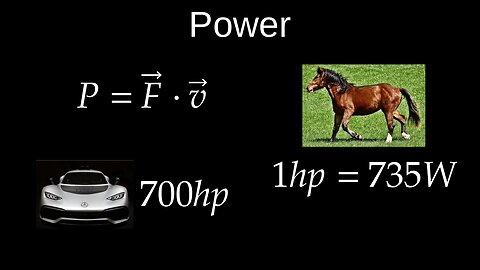
Power, Horsepower, Rate of Work - Physics (Mechanics)
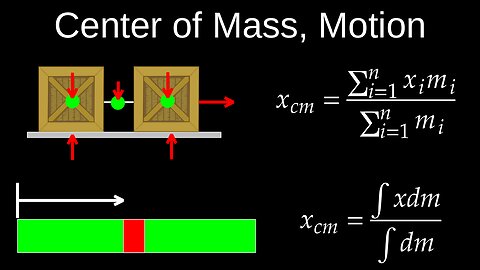
Center of Mass vs Gravity, Discrete Bodies, Integral, Linear Motion - Physics (Mechanics)
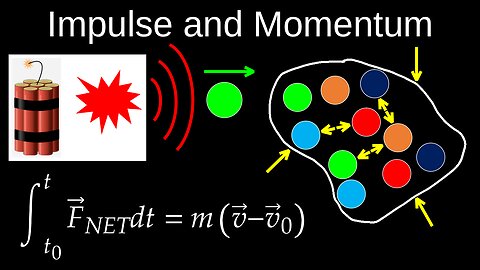
Impulse and Momentum, Theorem, Particle, Systems, Average Force, Application - Physics C (Mechanics)
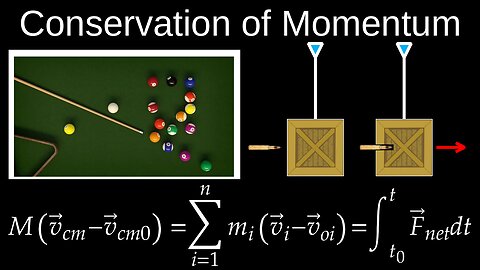
Conservation of Linear Momentum, 2D, Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - Physics (Mechanics)
Vector Cross Product - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Right Hand Rule - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Determinant - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Proof, 2D Cartesian Coords - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Example - Physics
Torque - Physics
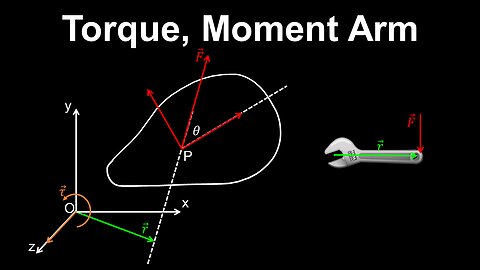
Torque, Moment Arm - Physics
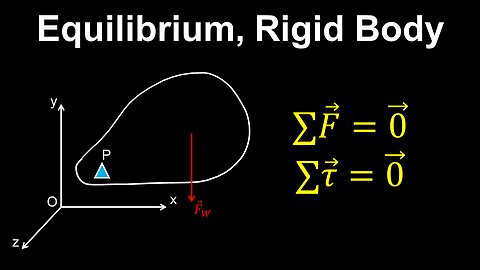
Equilibrium, Rigid Body - Physics
Equilibrium, Rigid Body, Example - Physics
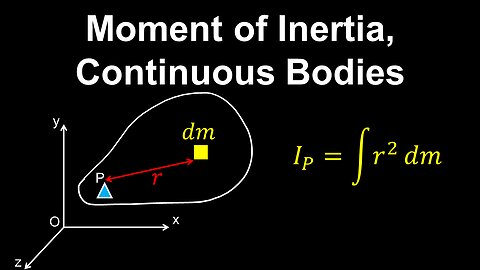
Moment of Inertia, System of Particles - Physics
Moment of Inertia, Rigid Body - Physics
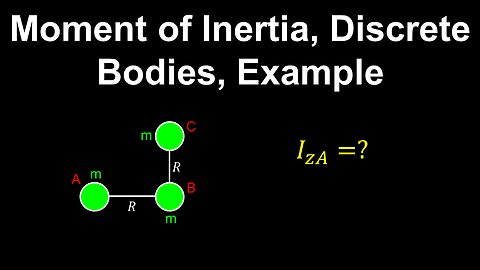
Moment of Inertia, System of Particles, Example - Physics
Moment of Inertia, Examples - Physics
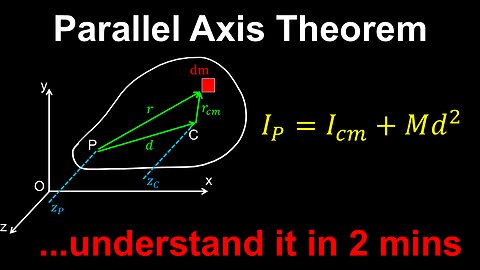
Parallel-Axis Theorem, Moment of Inertia - Physics
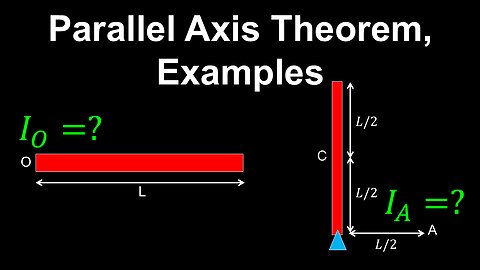
Parallel Axis Theorem, Moment of Inertia, Examples - Physics
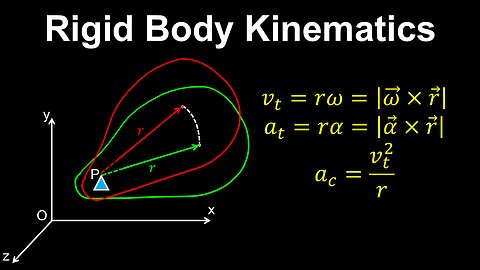
Rigid Body Kinematics, Rotation - Physics
Rotational Kinematics, Big Five - Physics
Rotational Kinematics, Examples - Physics
Rolling Motion, No Slip - Physics
Rotational Dynamics, Energy - Physics
Angular Momentum, Spin, Orbital, Conservation - Physics
Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion - Physics
Simple Harmonic Motion, Solutions to ODE - Physics
Gravitational Forces, Newton's Law of Gravitation - Physics
Kepler's Laws, Satellite Orbits, Experimental Data - Physics
Gravitational Potential Energy, Escape Speed - Physics
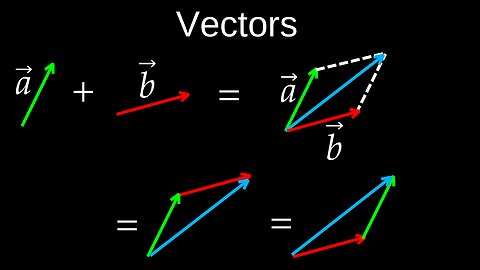
Vectors, Addition, Scaling, Negation, Subtraction, Coord Systems - Physics (Mechanics)
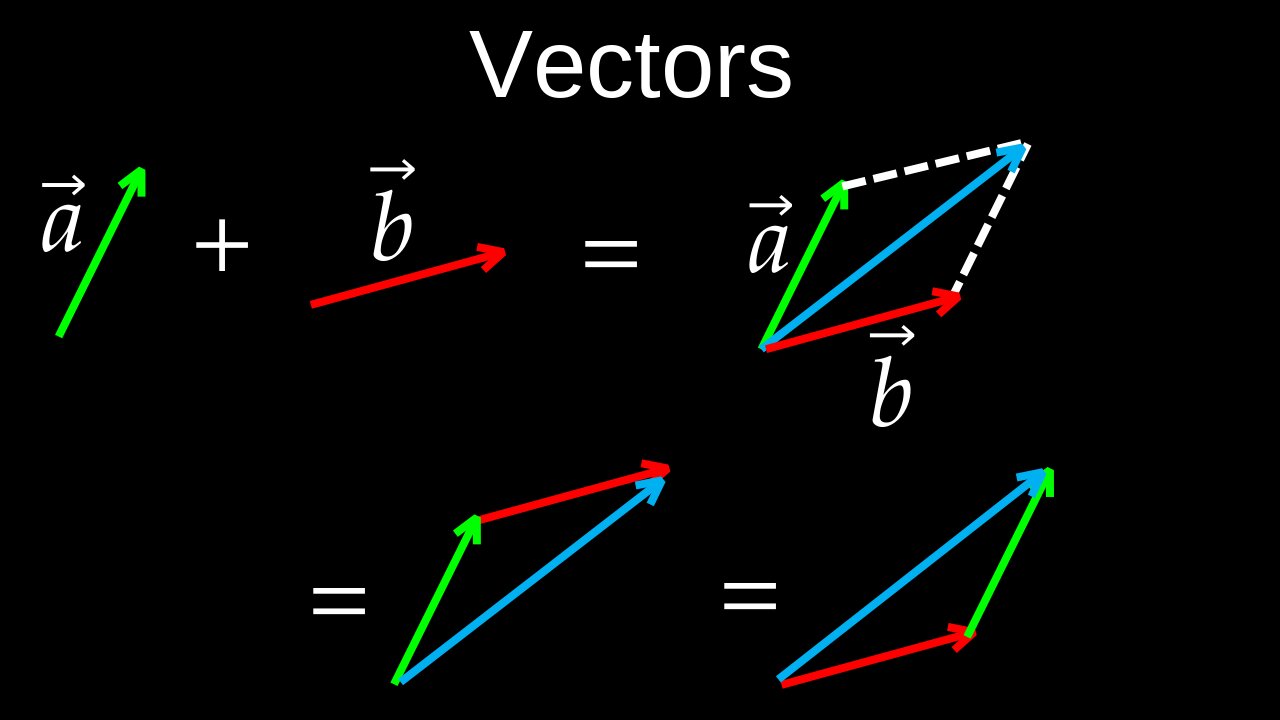
A vector is a mathematical and physical quantity with both magnitude (size) and direction. It is often represented graphically as a directed line segment, with the length of the arrow representing its magnitude and the arrowhead indicating its direction. Vectors are used in fields like physics and engineering to represent quantities such as velocity, acceleration, and force, and can be expressed in components as ordered lists of numbers (e.g., \([x,y]\) in 2D or \([x,y,z]\) in 3D).
💡Key characteristics
• Magnitude: The length of the vector, which indicates its size or intensity. For example, a force of \(60\) Newtons has a magnitude of \(60\).
• Direction: The way the vector points. In physics, this is crucial for quantities like velocity, which can be represented as "how fast" and "in what direction" an object is moving.
• Representation:
⚬Geometrically: As an arrow with a starting point (tail) and an ending point (head).
⚬Algebraically: As an ordered list of numbers called components, such as \([x,y]\) for a 2D vector or \([x,y,z]\) for a 3D vector.
• Notation:
⚬Boldface letters (e.g., u).
⚬A letter with an arrow above it (e.g., \(\vec{u}\)).
⚬A tilde underneath (e.g., \(\overset{\sim }{u}\)).
💡Applications and other meanings
• Physics and Engineering: Crucial for describing forces, velocity, acceleration, and other physical phenomena.
• Linear Algebra: Vectors are a fundamental concept, forming the basis for vector spaces, where vectors can be added together and multiplied by scalars (real numbers).
• Computer Science: Used to represent data, such as a list of features for a house price model.
• Other fields: The term "vector" can have other meanings, such as a carrier of a disease-causing agent or a DNA molecule used in genetic engineering.
💡Worksheets are provided in PDF format to further improve your understanding:
• Questions Worksheet: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1pD8nvbATuuSwvLF_nueB2KSc685rnQKr/view?usp=drive_link
• Answers: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SYKZihxmNSOL5K4ZQI663PIthUBqC9hs/view?usp=drive_link
💡Chapters:
00:00 Adding vectors
01:23 Scaling and negation
02:50 Subtracting vectors
03:59 Representing vectors in different coordinate systems
🔔Don’t forget to Like, Share & Subscribe for more easy-to-follow Calculus tutorials.
🔔Subscribe: https://rumble.com/user/drofeng
_______________________
⏩Playlist Link: https://rumble.com/playlists/d3cTgspk0Ro
_______________________
💥 Follow us on Social Media 💥
🎵TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@drofeng?lang=en
𝕏: https://x.com/DrOfEng
🥊: https://youtube.com/@drofeng
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Steven Crowder
1 hour agoIt's Time to Annex Canada
40,464 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Culture War with Tim Pool
28 minutes agoDEBATE: Islam Is TAKING OVER the West, America Is A CHRISTIAN NATION | The Culture War Podcast
1,495 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Rubin Report
31 minutes agoListen to Room Go Quiet as Rubio Says the Ugly Truth About Iran
1,437 watching -

BonginoReport
2 hours agoWho is Behind the Assaults on ICE? | Episode 205 - 01/16/26 VINCE
47.9K72 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
13 hours agoLIVE & BREAKING NEWS! | FRIDAY 1/16/26
4,123 watching -
 1:36:46
1:36:46
Graham Allen
2 hours agoTERRORISM IN AMERICA | Trump’s Presidency May Hinge on the Insurrection Act
121K469 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Badlands Media
5 hours agoBadlands Daily: 1/16/26
3,806 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Matt Kohrs
11 hours agoPAYDAY FRIDAY: Live Day Trading OPEX Chaos
457 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Big Mig™
1 hour agoTrumpCare, The Great Healthcare Plan LFG!
4,190 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
DoldrumDan
7 hours agoDEPTH 5 WINSTREAK STARTS NOW NIGHTREIGN MELEE IRONEYE
135 watching