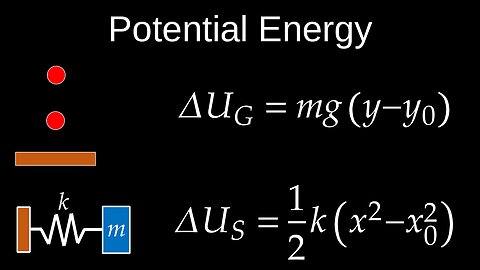Premium Only Content
Vectors Vs Scalars, Displacement, Distance, Velocity, Speed, Acceleration - Physics (Mechanics)
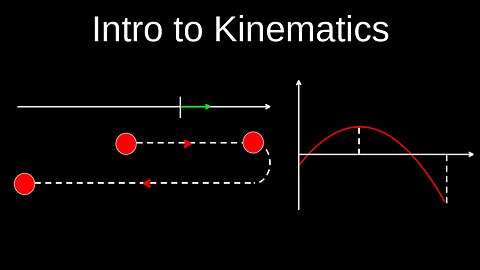
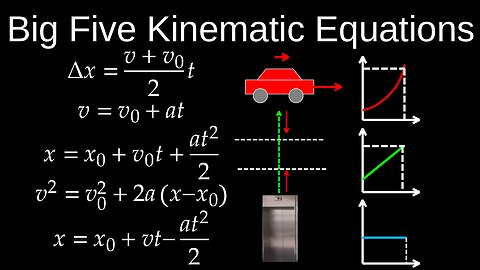
Big Five Kinematics, Uniform Acceleration, How to Select, Intervals, Objects - Physics (Mechanics)
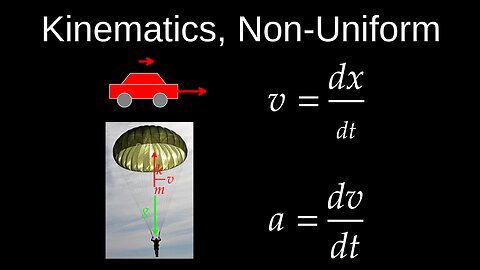
Kinematics, Non-Uniform Motion, Non-Constant Acceleration, 1D Motion - Physics (Mechanics)
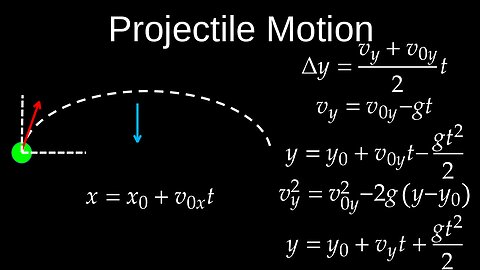
Projectile Motion, Kinematics, 2D Motion, Problems, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
Reference Frames, Relative Motion, Velocity, Vectors, Questions, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
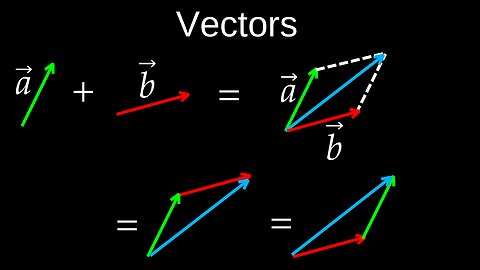
Vectors, Addition, Scaling, Negation, Subtraction, Coord Systems - Physics (Mechanics)
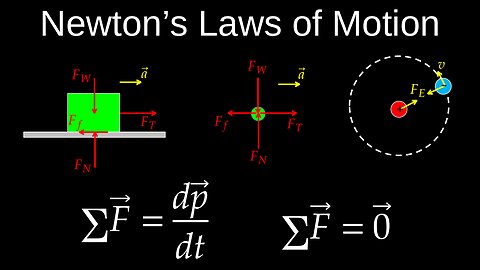
Newton's Second Law of Motion, First Law, Equations, Worksheet, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
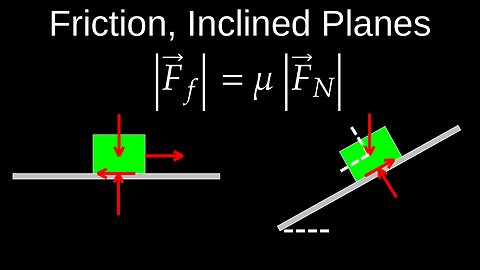
Friction, Resistive Force, Equation, Inclined Plane Motion, Examples - Physics (Mechanics)
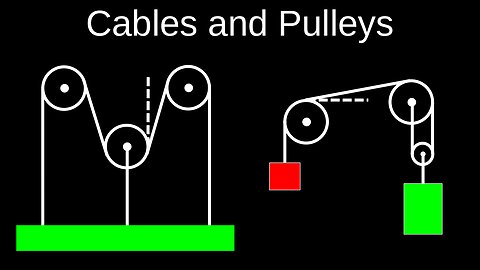
Cables and Pulleys, Massless, Atwood Machines, Free Body Diagrams - Physics (Mechanics)
Resistive Forces, Drag, Terminal Velocity, Example - Physics (Mechanics)
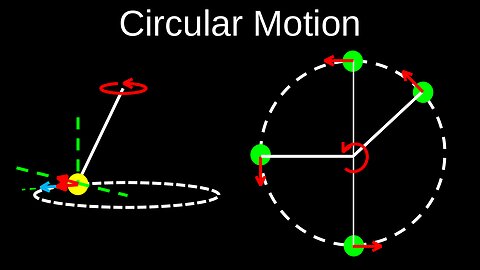
Circular Motion, Centripetal Acceleration, Vertical, Horizontal, Banked - Physics (Mechanics)
Newton's Third Law of Motion, Equal and Opposite Forces, Action Reaction Pairs - Physics (Mechanics)
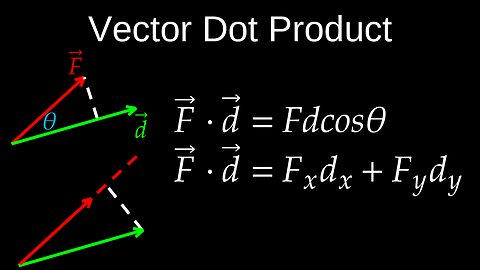
Vector Dot Product, Commutativity, Projection, Visualization, Proof - Physics (Mechanics)
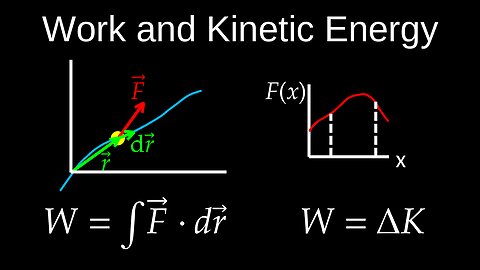
Work of a Force, Dot Product, Integral, Work Energy Theorem, Kinetic Energy - Physics (Mechanics)
Potential Energy, Gravity, Elastic, Spring, Conservative Forces, Functions - Physics (Mechanics)
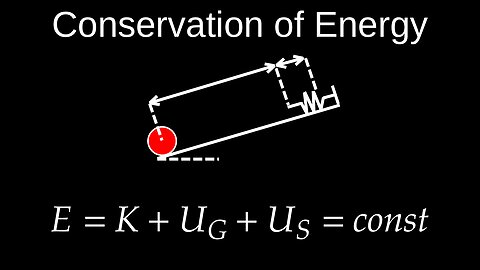
Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Conservative Systems - Physics (Mechanics)
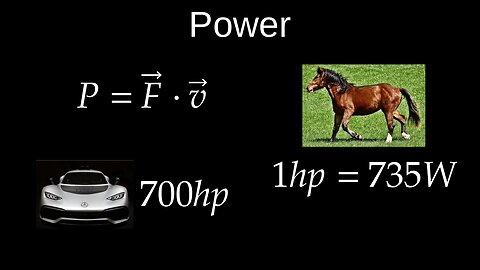
Power, Horsepower, Rate of Work - Physics (Mechanics)
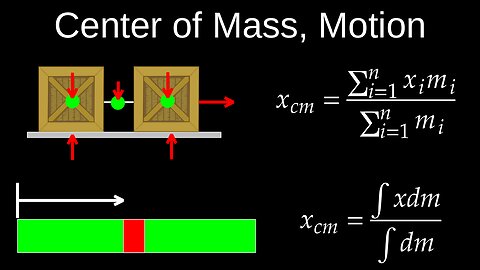
Center of Mass vs Gravity, Discrete Bodies, Integral, Linear Motion - Physics (Mechanics)
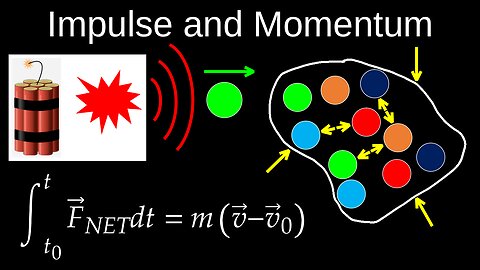
Impulse and Momentum, Theorem, Particle, Systems, Average Force, Application - Physics C (Mechanics)
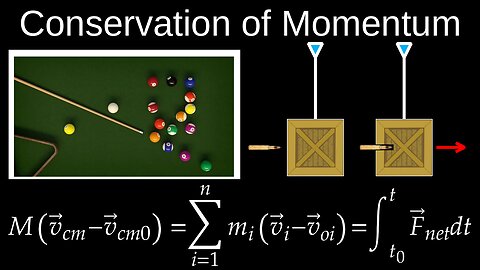
Conservation of Linear Momentum, 2D, Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - Physics (Mechanics)
Vector Cross Product - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Right Hand Rule - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Determinant - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Proof, 2D Cartesian Coords - Physics
Vector Cross Product, Example - Physics
Torque - Physics
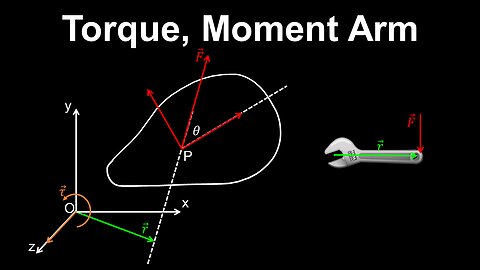
Torque, Moment Arm - Physics
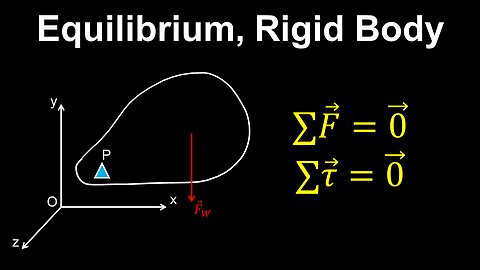
Equilibrium, Rigid Body - Physics
Equilibrium, Rigid Body, Example - Physics
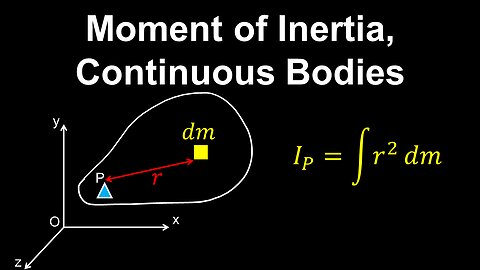
Moment of Inertia, System of Particles - Physics
Moment of Inertia, Rigid Body - Physics
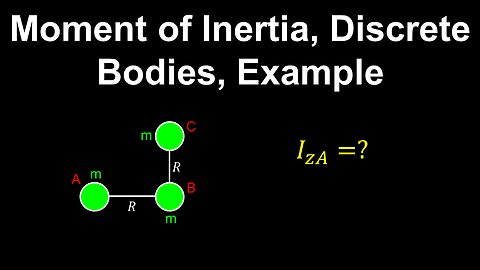
Moment of Inertia, System of Particles, Example - Physics
Moment of Inertia, Examples - Physics
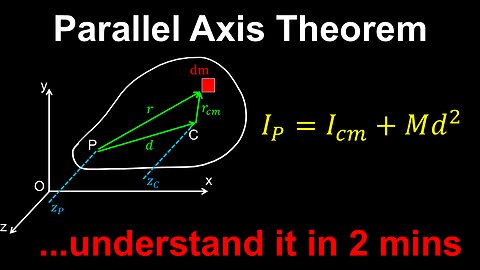
Parallel-Axis Theorem, Moment of Inertia - Physics
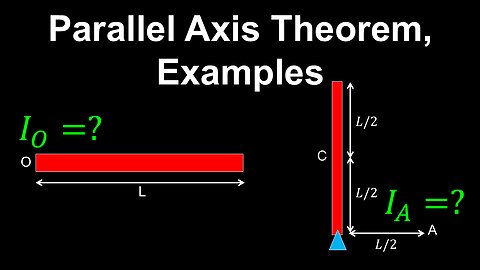
Parallel Axis Theorem, Moment of Inertia, Examples - Physics
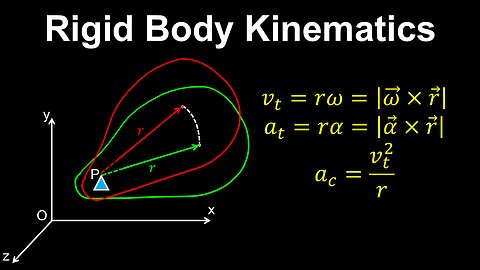
Rigid Body Kinematics, Rotation - Physics
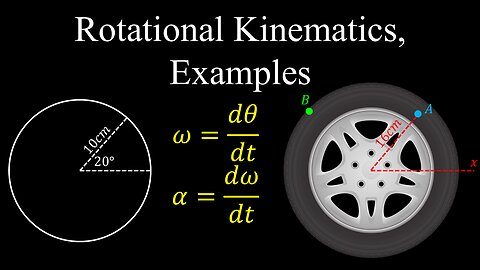
Rotational Kinematics, Big Five - Physics
Rotational Kinematics, Examples - Physics
Rolling Motion, No Slip - Physics
Rotational Dynamics, Energy - Physics
Angular Momentum, Spin, Orbital, Conservation - Physics
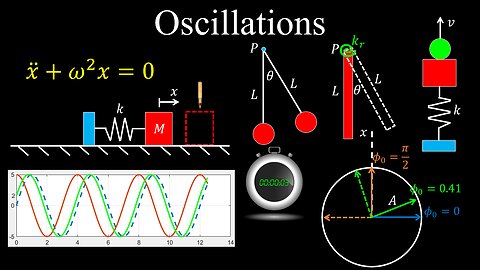
Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion - Physics
Simple Harmonic Motion, Solutions to ODE - Physics
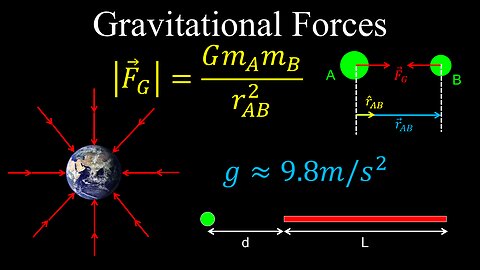
Gravitational Forces, Newton's Law of Gravitation - Physics
Kepler's Laws, Satellite Orbits, Experimental Data - Physics
Gravitational Potential Energy, Escape Speed - Physics
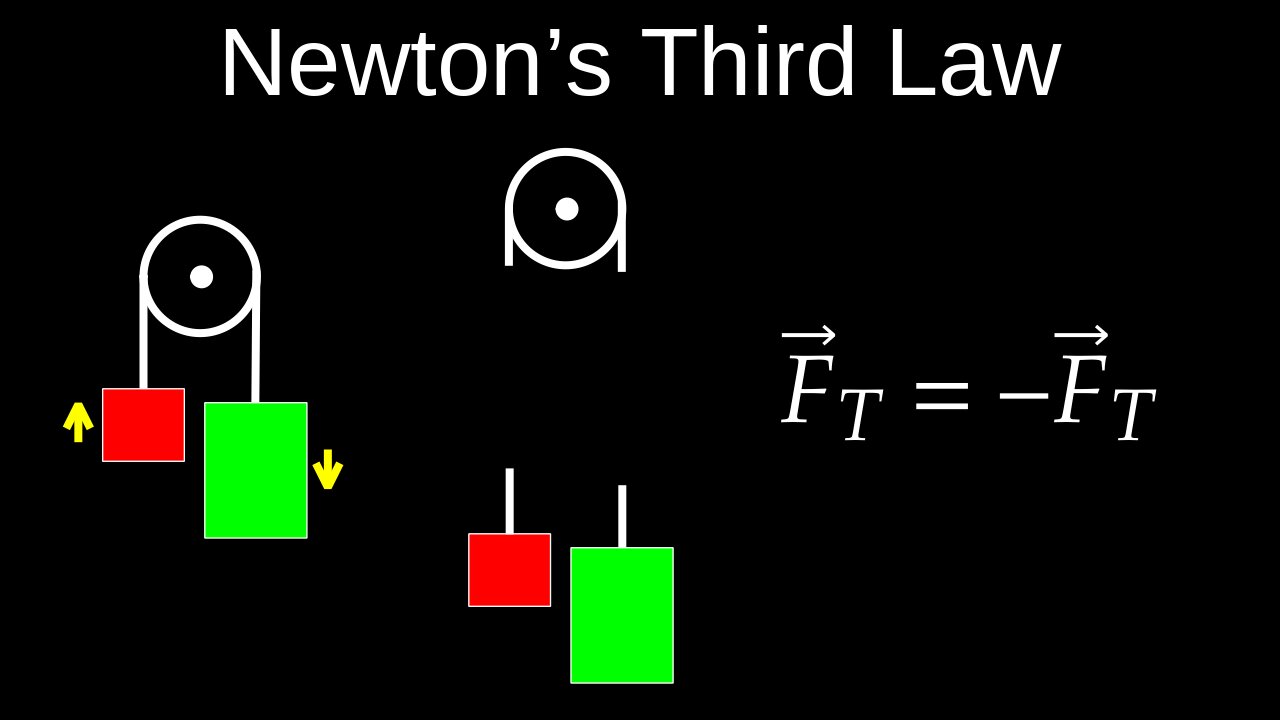
Newton's Third Law of Motion, Equal and Opposite Forces, Action Reaction Pairs - Physics (Mechanics)
Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. These forces are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction and always occur in pairs, acting on different objects.
💡Key concepts
• Action and reaction forces are a pair: Forces do not exist in isolation; they always come in pairs.
• Forces are equal in magnitude: The strength of the force is the same for both the action and the reaction. For example, if you push a wall with \(10\) pounds of force, the wall pushes back on you with \(10\) pounds of force.
• Forces are opposite in direction: The forces are always in opposite directions.
• Forces act on different objects: The action force acts on one object, and the reaction force acts on the second object. Therefore, the forces do not cancel each other out. For instance, when a boxer punches a bag, the boxer's fist applies a force to the bag, and the bag applies an equal and opposite force back on the fist.
• Example: A book on a table: A book on a table exerts a downward force due to its weight. The table exerts an equal and upward force on the book to support it.
💡Worksheets are provided in PDF format to further improve your understanding:
• Questions Worksheet: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1pD8nvbATuuSwvLF_nueB2KSc685rnQKr/view?usp=drive_link
• Answers: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SYKZihxmNSOL5K4ZQI663PIthUBqC9hs/view?usp=drive_link
💡Chapters:
00:00 Newton's third law
01:35 Worked example
🔔Don’t forget to Like, Share & Subscribe for more easy-to-follow Calculus tutorials.
🔔Subscribe: https://rumble.com/user/drofeng
_______________________
⏩Playlist Link: https://rumble.com/playlists/d3cTgspk0Ro
_______________________
💥 Follow us on Social Media 💥
🎵TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@drofeng?lang=en
𝕏: https://x.com/DrOfEng
🥊: https://youtube.com/@drofeng
-
 42:01
42:01
Man in America
12 hours agoIs the Globalist Plan to Collapse America and Blame it on Trump? w/ Alex Newman
162K33 -
 2:51:54
2:51:54
FreshandFit
11 hours agoMen Cannot Get Pregnant?
54K8 -
 2:51:00
2:51:00
TimcastIRL
7 hours agoAnti-ICE Extremists LOOT DHS Vehicles, Steal Weapons, Trump Warns INSURRECTION | Timcast IRL
313K118 -
 40:51
40:51
The Quartering
6 hours agoA RECKONING IN MINNESOTA & ANOTHER TRANS SCHOOL ATTACK!
37.4K53 -
 31:39
31:39
Robbi On The Record
4 days ago $8.86 earnedA Firsthand Account of Nigeria’s Christian Genocide | Judd Saul
45.5K8 -
 56:27
56:27
Flyover Conservatives
1 day agoThe Dark Economics Behind Organ Transplants, Plastics, and Human Health - Kim Bright | FOC Show
41.3K -
 4:55:21
4:55:21
Drew Hernandez
1 day agoLEFTIST TERRORISTS RAID & LOOT FEDERAL LAW ENFORCEMENT VEHICLES: STILL NO INSURRECTION ACT
64.5K15 -
 42:43
42:43
Sarah Westall
7 hours agoThe Psychological War Online - How They Target You | Eric Meder
45.3K3 -
 1:29:35
1:29:35
DLDAfterDark
5 hours ago $2.35 earnedBadge Cam Shootings - Let's Watch Some Semi Precious Metals Fly!
35.6K -
 2:16:00
2:16:00
megimu32
5 hours agoOTS: THEY STOLE THAT… AND IT STILL WASN’T BETTER!
39.2K4