Premium Only Content
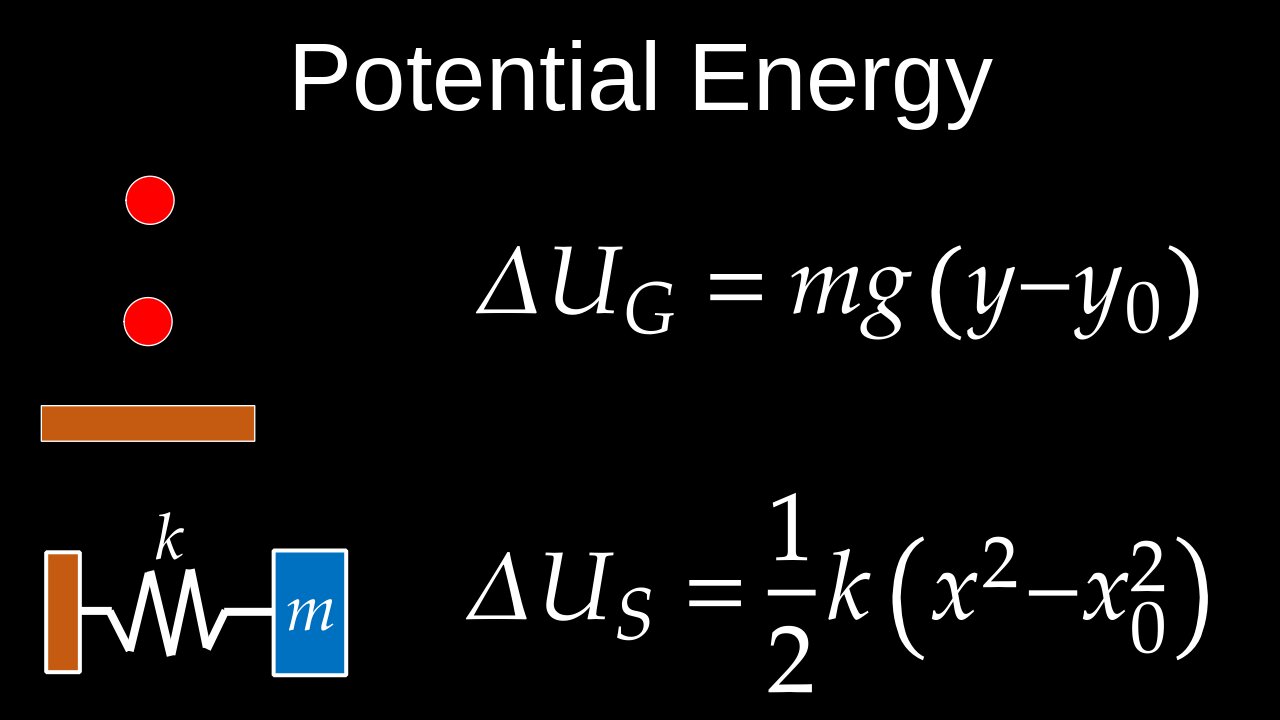
Potential Energy, Gravity, Elastic, Spring, Conservative Forces, Functions - Physics (Mechanics)
Potential energy is stored energy within a physical system, dependent on the relative position or arrangement of its interacting parts. This stored energy has the "potential" to do work and is one of the two main forms of energy, the other being kinetic energy (energy of motion). Potential energy arises from systems involving conservative forces, such as gravity, electric fields, and spring forces.
💡Types and Examples
Potential energy manifests in several forms:
• Gravitational Potential Energy: Energy stored due to an object's vertical position or height within a gravitational field. A rock on the edge of a cliff or water behind a dam are classic examples. The formula for an object near Earth's surface is (PE=mgh), where (m) is mass, (g) is gravitational acceleration, and (h) is height above a reference point.
• Elastic Potential Energy: Energy stored in objects that are stretched or compressed, such as springs, rubber bands, or a drawn archer's bow. The more an object is deformed, the more elastic potential energy it stores.
• Chemical Potential Energy: Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. This energy is released during chemical reactions, such as when burning wood, digesting food, or in batteries producing electricity.
• Electrical Potential Energy: Energy resulting from the position or configuration of electrically charged objects within an electric field. Lightning is a sudden release of a vast amount of stored electrical potential energy.
• Nuclear Potential Energy: Energy stored within the nucleus of an atom, bound by the strong nuclear force. This energy can be released during nuclear fission or fusion reactions.
💡Relationship with Kinetic Energy
Potential energy and kinetic energy are two sides of the same coin in mechanical systems. They are constantly converting back and forth, while the total energy of the system remains conserved (the law of conservation of energy). For example, a roller coaster car at the peak of a large hill has maximum potential energy and minimal kinetic energy. As it descends, its potential energy converts into kinetic energy, causing it to speed up. The process reverses as it climbs the next hill.
💡Worksheets are provided in PDF format to further improve your understanding:
• Questions Worksheet: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1D6ggRPXcqhSpXFgb6hrKiJSP6S_uFthb/view?usp=drive_link
• Answers: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PMk7nlIaV6aBEn0eO2iBPkxqAYWKJzSj/view?usp=drive_link
💡Chapters:
00:00 Gravitational potential energy
01:31 Elastic potential energy
03:07 Conservative forces
04:48 Dissipative forces
06:31 Potential energy functions and diagrams
08:42 Worked examples
🔔Don’t forget to Like, Share & Subscribe for more easy-to-follow Calculus tutorials.
🔔Subscribe: https://rumble.com/user/drofeng
_______________________
⏩Playlist Link: https://rumble.com/playlists/d3cTgspk0Ro
_______________________
💥 Follow us on Social Media 💥
🎵TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@drofeng?lang=en
𝕏: https://x.com/DrOfEng
🥊: https://youtube.com/@drofeng
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Dr Disrespect
3 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - ARC RAIDERS - BURIAL CITY KILLAS
1,564 watching -
 1:36:33
1:36:33
Steve-O's Wild Ride! Podcast
6 days ago $1.83 earnedMaynard James Keenan and Steve-O Look For Trouble | Wild Ride #278
9.88K3 -
 2:00:00
2:00:00
The Mel K Show
3 hours agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K - Chaos Manipulation and the Media 1-28-26
32.5K6 -
 LIVE
LIVE
StoneMountain64
1 hour agoArc Raiders BUFFED the VENTATOR and IT'S BUSTED
100 watching -
 1:02:17
1:02:17
Timcast
3 hours agoIlhan Omar Attack HOAX??! GOP Says "ITS FAKE!"
173K87 -
 DVR
DVR
Sean Unpaved
1 day agoBills Hire JOE BRADY As Their Next Head Coach! | UNPAVED
34.6K3 -
 1:59:35
1:59:35
Steven Crowder
5 hours agoHoman to Minnesota - What This Means + MCU Infiltrates Signal
440K329 -
 1:08:32
1:08:32
The Rubin Report
4 hours ago‘Shark Tank’ Legend Notices Something in Minneapolis Others Refuse to See
57K55 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Wendy Bell Radio
7 hours agoThe Lamest Show On Earth
5,668 watching -
 1:00:59
1:00:59
BonginoReport
5 hours agoThey Just Said the Quiet Part Out Loud | Episode 213 - 01/28/26 VINCE
214K153