Premium Only Content

Mega-Regions - Easier Today
**Unified Resilient Habitat Engineering Codex**
**FOLM (Fractal Octo-Lux Modernism) System** for mega-region development.
- **Population Capacity:** Designed to support **7.92 billion people**, providing for a small global civilization footprint.
This description integrates the technical, spatial, temporal, ecological, and architectural aspects into a coherent vision of a future-ready, sustainable mega-region.
---
### Unified Resilient Habitat Engineering Codex: FOLM System for Global Mega-Region Development
The **Unified Resilient Habitat Engineering Codex** represents an ambitious, visionary framework for designing and sustaining a **Global Mega-Region** over a millennium-scale temporal horizon. It leverages advanced fractal geometry, cutting-edge materials science, and ecological integration to create a resilient, scalable, and aesthetically pure habitat system optimized for both human civilization and natural ecosystems.
---
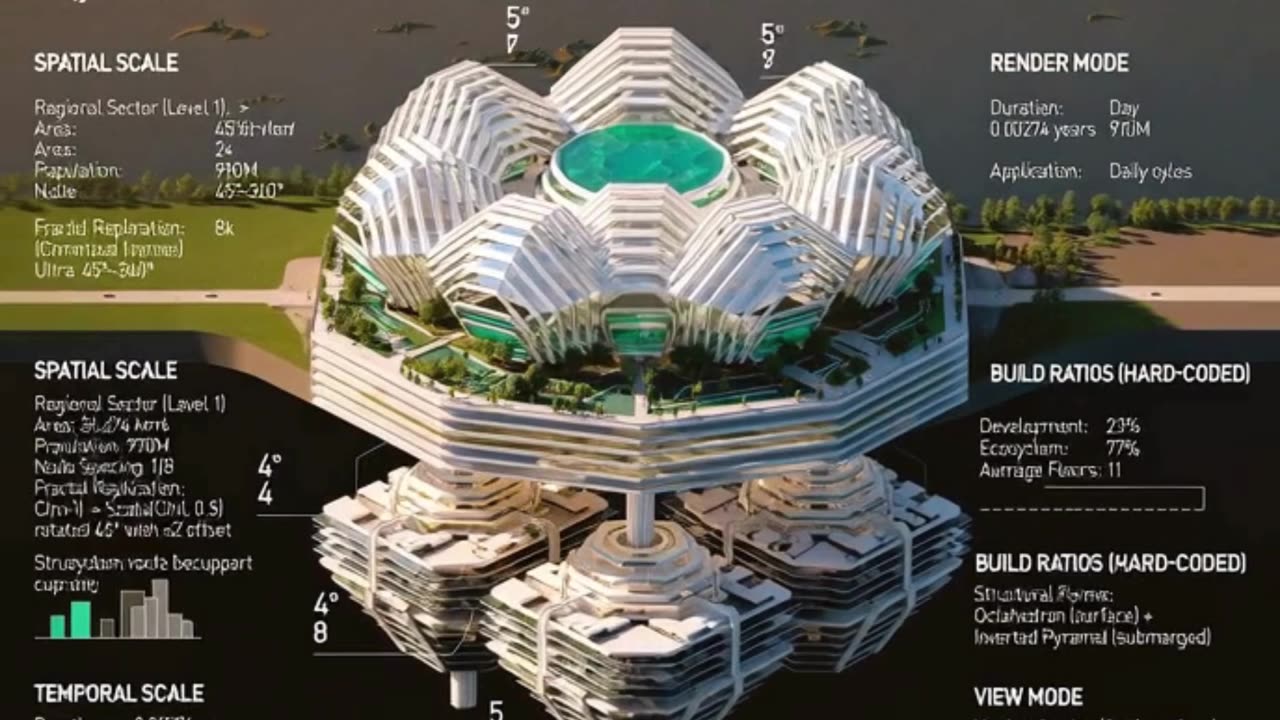
#### Spatial and Population Scale
- **Mega-Region Size:** Approximately **277,391 km²**, encompassing diverse biomes and urbanized zones.
- **Population Capacity:** Designed to support a tiny **7.92 billion people**, supporting a small global civilization.
- **Node Spacing:** Utilizes a fractal replication principle where habitat nodes are spaced with precise mathematical scaling, allowing for efficient resource distribution and spatial harmony.
- **Fractal Replication Formula:** Each subsequent fractal iteration is scaled by 0.5, rotated by 45°, and offset by √2, creating an intricate octagonal stellation pattern that balances density and openness.
---
#### Temporal Scale and Legacy
- **Duration:** The system is engineered for **1000 years**, emphasizing longevity, adaptability, and intergenerational equity.
- **Civilizational Legacy:** It is conceived not just as infrastructure but as a **lasting legacy**, ensuring that future generations inherit a habitat that is both functional and inspiring.
---
#### Built Environment and Ecosystem Integration
- **Development Ratio:** Only **23%** of the land area is allocated to built infrastructure, prioritizing human habitats, transit, and service nodes.
- **Ecosystem Preservation:** A dominant **77%** is dedicated to natural ecosystems, including reforested areas, water bodies, and terraformed desert zones, ensuring biodiversity and climate resilience.
- **Average Building Height:** Structures average **11 floors**, balancing vertical density with human scale.
- **Architectural Forms:** The built environment features **octahedron surface structures** combined with **inverted pyramids submerged below ground or water**, creating a dynamic interplay between above-ground and subterranean spaces.
---
#### Architectural and Material Aesthetics
- **Style:** The system embodies **Fractal Octo-Lux Modernism (FOLM)** — a style characterized by abstract architectural purity, crystalline geometry, and octagonal symmetry.
- **Materials:** Uses high-tech, sustainable materials such as **crystalline white-gold and emerald-malachite composites**, **mirror-polished titanium facades**, and **diamond-etched glass** to achieve durability, reflectivity, and aesthetic brilliance.
- **Lighting:** Structures are rendered with **cinematic golden-hour rim lighting** to highlight the crystalline geometry and create a hyper-realistic visual experience.
- **Visual Mode:** The habitat is represented as a **water terraforming system**, featuring sky reservoirs, descending aqueducts, and glowing cyan water-flow lines, showcasing a seamless integration of water management and habitat design.
---
#### Functional Systems and Infrastructure
- **Water Terraforming:** Multi-layered water systems include atmospheric water harvesters, subterranean water chambers, and mid-level transit-aqueduct layers, ensuring sustainable water capture, storage, and distribution in arid environments.
- **Transit Grid:** A **45° octagonal transit grid** facilitates efficient movement of people and goods, integrated with water infrastructure to optimize space and resource use.
- **Automated Systems:** The mega-region employs advanced automation for ecosystem management, transit coordination, and environmental monitoring, reducing human labor and increasing precision.
---
#### Mathematical and Planning Frameworks
- **FOLM Formula:** The system’s efficiency and aesthetic quality are quantified by a composite function:
\[
F(x,y,z) = 1.1 \times (0.95BE + 0.60FE + 0.80CE + 0.45AE + 0.98MAE + 0.92M + 0.98L + 0.75G + 0.30AC + 0.95MA)
\]
where variables represent:
- BE: Built Environment
- FE: Fractal Efficiency
- CE: Circulation Efficiency
- AE: Architectural Elegance
- MAE: Material Aesthetic Efficiency
- M: Mechanical systems
- L: Lighting
- G: Green space integration
- AC: Automated Control
- MA: Maintenance Automation
- **FATI Temporal Validation:** The system adheres to the **FATI Core Validation** for long-term sustainability, ensuring a minimum planning horizon of 20 years and monitoring concentration and impact thresholds to prevent ecological overshoot.
---
#### Sustainability and Ecological Harmony
- **Desert Optimization:** The system is tailored for harsh desert environments, transforming arid landscapes through water terraforming and reforestation, recovering ecosystems while supporting dense human populations.
- **Ecosystem Dominance:** By dedicating 77% of the area to ecological zones, the system prioritizes carbon sequestration, biodiversity, and climate regulation.
---
### Summary
The **Unified Resilient Habitat Engineering Codex’s FOLM System** offers a visionary blueprint for the future of mega-region development. It harmonizes fractal geometry, advanced materials, ecological stewardship, and millennial-scale planning into a coherent, scalable, and resilient habitat system.
This model transcends conventional urban design by integrating water terraforming, architectural purity, and ecosystem dominance, creating a living infrastructure that supports a global civilization while honoring the planet’s natural rhythms.
---
"Mega-Region Modeling Easier Today"
How advances have made it simpler to model mega-regions
Large interconnected metropolitan areas that span multiple cities and often cross state or national boundaries.
These mega-regions are critical for urban planning, infrastructure development, transportation, environmental management, and economic forecasting.
Here’s a detailed overview of why and how mega-region modeling is easier today:
What Are Mega-Regions?
Mega-regions are vast networks of cities and towns linked by economic, community, and infrastructure ties.
Examples include the Northeast Corridor in the US (Boston to Washington, D.C.), the Pearl River Delta in China, and the European Blue Banana.
Modeling these regions helps planners understand complex interactions across large geographic and administrative areas.
Why Mega-Region Modeling Matters
Infrastructure planning: Coordinating transportation, energy, and water systems.
Environmental sustainability: Managing resources and reducing pollution across borders.
Economic development: Understanding labor markets and trade flows.
Disaster preparedness: Coordinating emergency response over large areas.
Why Modeling Mega-Regions Is Easier Today
Advances in Data Availability and Technology
Big Data: Massive datasets from mobile devices, sensors, satellite imagery, to allow real-time framing, traffic flows, and environmental conditions.
GIS and Remote Sensing: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and satellite data provide detailed spatial data to model land use, urban growth, and natural resources.
Open Data Initiatives: Governments and organizations increasingly share data openly, improving access to transportation, demographic, and environmental datasets.
Improved Computational Power
Modern supercomputers and cloud computing platforms can process complex simulations involving millions of variables faster and more accurately.
Parallel computing enables simultaneous processing of multiple scenarios, enhancing predictive modeling.
Advanced Modeling Techniques
Agent-Based Models: Simulate the behavior of individuals or entities to capture emergent phenomena in urban systems.
Machine Learning and AI: Help identify patterns, optimize models, and improve forecasting accuracy.
Integrated Models: Combine transportation, land use, economic, and environmental models for holistic analysis.
Collaborative Platforms and Tools
Online platforms enable collaboration among governments, researchers, and stakeholders.
Tools : UrbanSim, MATSim, and others provide frameworks specifically designed for large-scale urban and regional modeling.
Policy and Planning Frameworks
Recognition of mega-regions’ importance encourages coordinated policies and data sharing agreements, facilitating integrated modeling efforts.
Example: Sustainable Mega-Region Planning
In the US, the Northeast Megaregion uses integrated transportation and land-use models to reduce carbon emissions by optimizing transit networks and promoting compact urban development, showing how easier modeling leads to actionable sustainability strategies.
-
 DVR
DVR
Timcast
1 hour agoDemocrats EXPAND Insurgency To more States As Trump SURRENDERS Minnesota
34K78 -
 1:58:17
1:58:17
Steven Crowder
4 hours agoIs Trump Backing Down or Doubling Down in Minnesota: Special Guest Nick Sortor
319K228 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Side Scrollers Podcast
2 hours agoSide Scrollers Podcast Live | Tuesday January 27th 2026
649 watching -
 UPCOMING
UPCOMING
Sean Unpaved
1 hour agoBills Hire JOE BRADY As Their Next Head Coach! | UNPAVED
92 -
 1:06:08
1:06:08
The Rubin Report
2 hours agoIlhan Omar Finally Got Scared After Investigation Into Her $5M Winery Just Went Viral
19.8K45 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Wendy Bell Radio
4 hours agoTrump to Tampon Tim: It Stops Now.
6,722 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
16 hours agoLIVE & BREAKING NEWS! | TUESDAY 1/27/26
3,701 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Viss
2 hours ago🔴(LIVE) - 1V3 SOLO VS SQUADS AGAINST ALL ODDS! | ARC RAIDERS HEADWIND
229 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
TheAlecLaceShow
1 hour agoGuests: Roger Stone, Rep. Burlison, Rep. McCormick, Rep. Gill | The Alec Lace Show
50 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
GritsGG
1 hour agoCamo Grind Continues #1 Warzone Victory Leaderboard 1060+ Ws!!🔥
45 watching